Microsoft - SC-300: Microsoft Identity and Access Administrator
Sample Questions
Question: 381
Measured Skill: Implement authentication and access management (25–30%)
You have a Microsoft 365 subscription.
You need to create a Conditional Access policy that will use a Global Secure Access security profile. The solution must ensure that users are prevented from accessing websites that include the word gambling in the URL.
What should you do first?| A | Create a web content filtering policy. |
| B | Create a named location. |
| C | Configure the Adaptive Access settings. |
| D | Create a network security group (NSG). |
Correct answer: AExplanation:
Microsoft Entra Internet Access and Microsoft Entra Private Access comprise Microsoft's Security Service Edge (SSE) solution. Global Secure Access is the unifying term used for both Microsoft Entra Internet Access and Microsoft Entra Private Access. Global Secure Access is the unified location in the Microsoft Entra admin center.
Microsoft Entra Internet Access's first Secure Web Gateway (SWG) features include web content filtering based on domain names. Microsoft integrates granular filtering policies with Microsoft Entra ID and Microsoft Entra Conditional Access, which results in filtering policies that are user-aware, context-aware, and easy to manage.
There are several steps to configuring web content filtering. Take note of where you need to configure a Conditional Access policy.
- Enable internet traffic forwarding.
- Create a web content filtering policy.
- Create a security profile.
- Link the security profile to a Conditional Access policy.
- Assign users or groups to the traffic forwarding profile.
References:
What is Global Secure Access?
How to configure Global Secure Access web content filtering
Question: 382
Measured Skill: Plan and automate identity governance (25–30%)
You have an Azure subscription that is linked to a Microsoft Entra tenant. The tenant contains the groups shown in the following table.
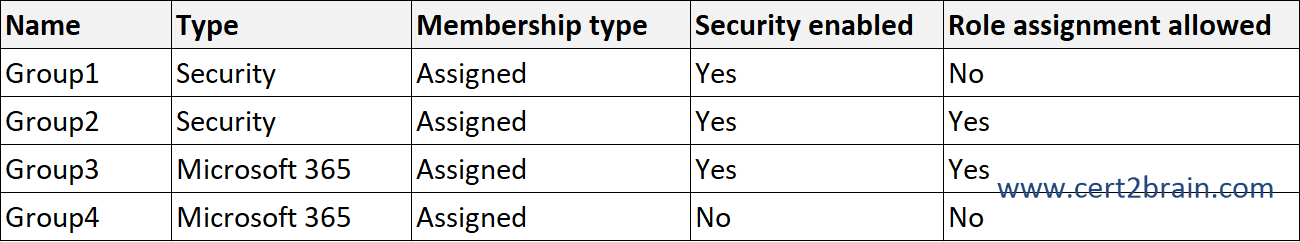
Which groups can you manage by using Privileged Identity Management (PIM)?| A | Group2 only |
| B | Group1 and Group2 only |
| C | Group2 and Group4 only |
| D | Group1, Group2, and Group3 only |
| E | Group1, Group2, Group3, and Group4 |
Correct answer: DExplanation:
Microsoft Entra ID allows you to grant users just-in-time membership and ownership of groups through Privileged Identity Management (PIM) for Groups. Groups can be used to control access to a variety of scenarios, including Microsoft Entra roles, Azure roles, Azure SQL, Azure Key Vault, Intune, other application roles, and third-party applications.
PIM for Groups is part of Microsoft Entra Privileged Identity Management – alongside with PIM for Microsoft Entra roles and PIM for Azure Resources, PIM for Groups enables users to activate the ownership or membership of a Microsoft Entra security group or Microsoft 365 group. Non-security enabled groups can't be enabled for role assignments and can't be managed by PIM for Groups. Groups can be used to govern access to various scenarios that include Microsoft Entra roles, Azure roles, Azure SQL, Azure Key Vault, Intune, other application roles, and third party applications.
With PIM for Groups you can use policies similar to ones you use in PIM for Microsoft Entra roles and PIM for Azure Resources: you can require approval for membership or ownership activation, enforce multifactor authentication (MFA), require justification, limit maximum activation time, and more. Each group in PIM for Groups has two policies: one for activation of membership and another for activation of ownership in the group.
References:
What is Microsoft Entra Privileged Identity Management?
Privileged Identity Management (PIM) for Groups
Question: 383
Measured Skill: Implement and manage user identities (20–25%)
You have a Microsoft Entra tenant named contoso.com that contains an enterprise application named App1.
A contractor uses the credentials of user1@outlook.com.
You need to ensure that you can provide the contractor with access to App1. The contractor must be able to authenticate as user1@outlook.com.
What should you do?| A | Implement Microsoft Entra Connect sync. |
| B | Create a guest user account in contoso.com. |
| C | Configure the External collaboration settings. |
| D | Run the New-MgUser cmdlet. |
Correct answer: BExplanation:
We should create a guest account for the contractor. With a Microsoft Entra B2B guest account, you can invite anyone to collaborate with your organization using their own work, school, or social account.
B2B collaboration is a capability of Microsoft Entra External ID that lets you collaborate with users and partners outside of your organization. With B2B collaboration, an external user is invited to sign in to your Microsoft Entra workforce tenant using their own credentials. This B2B collaboration user can then access the apps and resources you want to share with them. A user object is created for the B2B collaboration user in the same directory as your employees. B2B collaboration user objects have limited privileges in your directory by default, and they can be managed like employees, added to groups, and so on.
References:
Understand and manage the properties of B2B guest users
Quickstart: Add a guest user and send an invitation
Question: 384
Measured Skill: Implement authentication and access management (25–30%)
Your on-premises network contains an Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) domain. The domain contains a server named Server1 that runs Windows Server and hosts a shared folder named Share1. The domain contains 500 devices that run Windows 11.
You have a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription that syncs with the domain.
From Global Secure Access, you enable the Private access profile and deploy the Global Secure Access client to all the devices.
You need to ensure that the devices can connect to Share1 remotely by using Global Secure Access.
Which three actions should you perform in sequence?
(To answer move the appropriate actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.)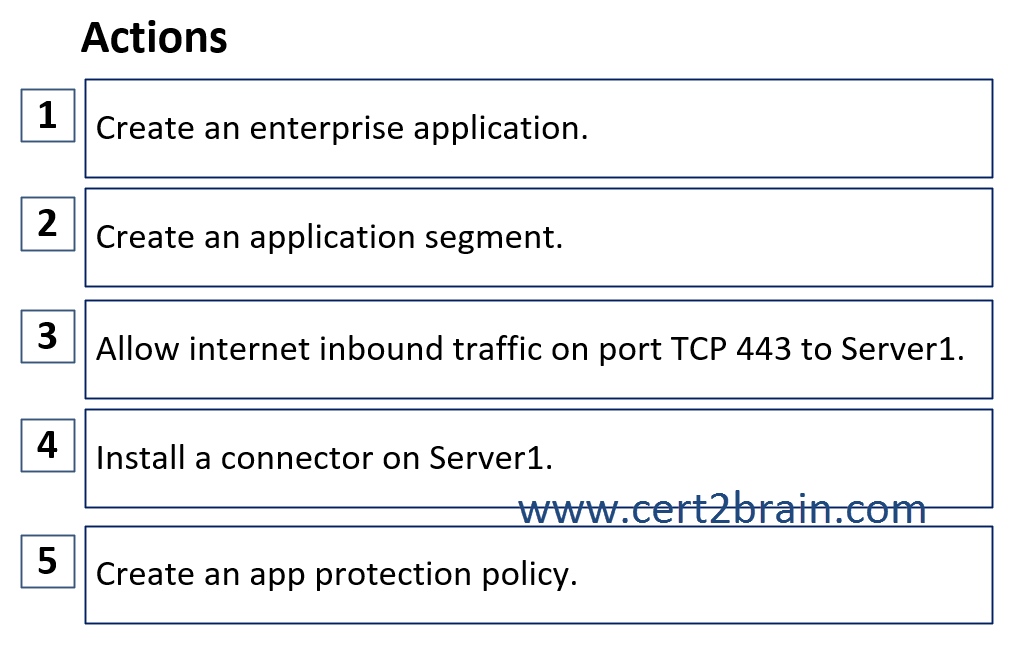
| A | Sequence: 1, 2, 5 |
| B | Sequence: 4, 3, 5 |
| C | Sequence: 4, 1, 2 |
| D | Sequence: 3, 2, 5 |
Correct answer: CExplanation:
Private Access provides two ways to configure the private resources that you want to tunnel through the service. You can configure Quick Access, which is the primary group of FQDNs and IP addresses that you want to secure. You can also configure a Global Secure Access app for per-app access, which allows you to specify a subset of private resources that you want to secure. The Global Secure Access app provides a granular approach to securing your private resources.
When you configure the Quick Access and Global Secure Access apps, you create a new enterprise application. The app serves as a container for the private resources that you want to secure. The application has its own Microsoft Entra private network connector to broker the connection between the service and the internal resource. You can assign users and groups to the app, and then use Conditional Access policies to control access to the app.
Microsoft Entra private network connector does require outbound connectivity on port 80 and port 443, but does not require inbound connectivity.
References:
Learn about Microsoft Entra Private Access
How to configure private network connectors for Microsoft Entra Private Access and Microsoft Entra application proxy
Microsoft Entra Private Access for on-prem users
Question: 385
Measured Skill: Implement authentication and access management (25–30%)
You have an Azure subscription named Sub1 that contains a resource group named RG1. RG1 contains two Azure key vaults named KV1 and KV2 that use Azure role-based access control (Azure RBAC).
The subscription contains the users shown in the following table.

KV1 contains a secret named Secret1. KV2 contains a secret named Secret2.
Which users can read the values of each secret?
(To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.)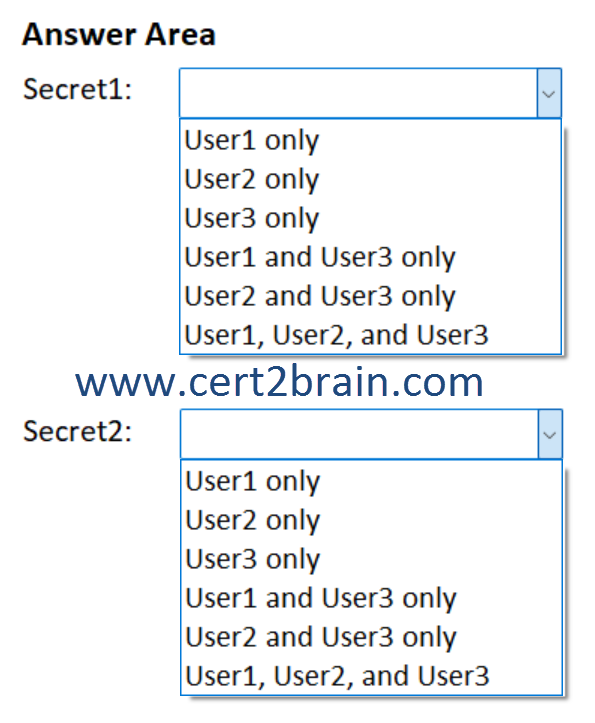
| A | Secret1: User1 only
Secret2: User1, User2, and User3 |
| B | Secret1: User2 only
Secret2: User3 only |
| C | Secret1: User3 only
Secret2: User2 and User3 only |
| D | Secret1: User1 and User3 only
Secret2: User1 only |
| E | Secret1: User2 and User3 only
Secret2: User2 only |
| F | Secret1: User1, User2, and User3
Secret2: User1 and User3 only |
Correct answer: DExplanation:
Azure RBAC allows users to manage keys, secrets, and certificates permissions, and provides one place to manage all permissions across all key vaults.
The Azure RBAC model allows users to set permissions on different scope levels: management group, subscription, resource group, or individual resources. Azure RBAC for key vault also allows users to have separate permissions on individual keys, secrets, and certificates.
User1 is a Key Vault Administrator scoped to Sub1. User1 can perform all data plane operations on KV1 and KV2 and all objects in them, including certificates, keys, and secrets.
User2 is a Key Vault Reader scoped to RG1. User2 can read metadata of KV1 and KV2 and its certificates, keys, and secrets. User2 cannot read any sensitive values such as secret contents or key material.
User3 is a Key Vault Secrets User scoped to KV1. User2 can read secret contents including secret portion of a certificate with private key only from KV1.
Reference: Provide access to Key Vault keys, certificates, and secrets with Azure role-based access control